In an industry devoted to the people who use our products, services, and applications, research is paramount. We ask questions. We take notes. We learn everything we can about the target audience, and then iteratively test our work throughout the design process.
UX research—or as it’s sometimes called, design research—serves many purposes throughout the design process. It helps us identify and prove or disprove our assumptions, find commonalities across our target audience members, and recognize their needs, goals, and mental models. Overall, research informs our work, improves our understanding, and make our work better.
In this Complete Beginner’s Guide, we’ll look at the many elements of design research, from interviews and observations, to usability testing and A/B testing. Readers will get a head start on how to use these design research techniques in their work, and improve experiences for all users.
Table of Contents
What is UX Research?
UX research encompasses a variety of investigative methods used to add context and insight to the design process. Unlike other sub-fields of UX, research did not develop out of some other field or fields. It merely translated from other forms of research. In other words, UX practitioners have borrowed many techniques from academics, scientists, market researchers, and others. However, there are still types of research that are fairly unique to the UX world.
The main goal of design research is to inform the design process from the perspective of the end user. It is research that prevents us from designing for one user: ourselves. It’s fairly well accepted that the purposes of UX and user-centered design are to design with the end-user in mind; and it’s research that tells us who that person is, in what context they’ll use this product or service, and what they need from us.
UX research has two parts: gathering data, and synthesizing that data in order to improve usability. At the start of the project, design research is focused on learning about project requirements from stakeholders, and learning about the needs and goals of the end users. Researchers will conduct interviews, collect surveys, observe prospects or current users, and review existing literature, data, or analytics. Then, iteratively throughout the design process, the research focus shifts to usability and sentiment. Researchers may conduct usability tests or A/B tests, interview users about the process, and generally test assumptions that will improve the designs.
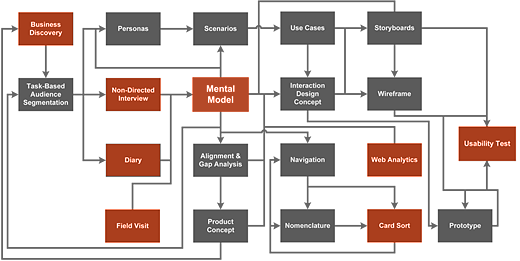
One example of a user research process, diagrammed. Young, Indi. 2008. Mental Models: Aligning Design Strategy with Human Behavior. New York: Rosenfeld Media.
We can also divide UX research methods into two camps: quantitative and qualitative.
- Quantitative research is any research that can be measured numerically. It answers questions such as “how many people clicked here” or “what percentage of users are able to find the call to action?” It’s valuable in understanding statistical likelihoods and what is happening on a site or in an app.
- Qualitative research is sometimes called “soft” research. It answers questions like “why didn’t people see the call to action” and “what else did people notice on the page?” and often takes the form of interviews or conversations. Qualitative research helps us understand why people do the things they do
Though researchers may specialize in specific types of interviews or tests, most are capable of conducting a wide variety of techniques. All user researchers collect valuable information that helps us design in an informed, contextual, user-centered manner.
Common Methodologies
The various types of UX research range from in-person interviews to unmoderated A/B tests (and everything in between), though they are consistent in that they all stem from the same key methodologies: observation, understanding, and analysis.
Observation
The first step to conducting research is learning to observe the world around us. Much like beginning photographers, beginning researchers need to learn how to see. They need to notice nervous tics that may signal that their interviewees are stressed or uncertain, and pick up on seemingly minor references that may reflect long-held beliefs or thoughts that should be further probed.
Observation may seem like a simple skill, but it can be clouded by unconscious biases—which everyone has. Design researchers train themselves to observe and take notes so that they can later find patterns across seemingly diverse groups of people.
Understanding
Much like observation, understanding is something we do all the time in our daily lives. We strive to understand our coworkers, our families, and our friends, often trying to grasp a point of contention or an unfamiliar concept. But for UX researchers, understanding has less to do with disagreements and more to do with mental models.
A mental model is the image that someone has in their mind when they think of a particular phrase or situation. For example, if someone owns an SUV, their mental model of “car” will likely differ from the mental model a smart car owner. The mental model informs the decisions we make; in the case of the car owners, when asked “how long does it take to drive to Winnipeg,” their answers will vary based on the gas mileage their vehicles get, among other things.
Design researchers need to understand the mental models of the people they interview or test, for two reasons. First, we all speak in shorthand at times. Researchers must recognize that shorthand based on the mental model of the speaker. Second, if the researcher can accurately identify the user’s mental model, he or she can share this information with the design team, and design to accommodate the model.
Analysis
Research on its own can be valuable, but in order to use the insights to inform design, it needs to be analyzed and ultimately presented to a larger team. Analysis is the process by which the researcher identifies patterns in the research, proposes possible rationale or solutions, and makes recommendations.
Some analysis techniques include creating personas or scenarios, describing mental models, or providing charts and graphs that represent statistics and user behaviors. Although the techniques described here are focused predominantly on conducting research, it’s important to remember that research is only valuable if it is shared. It does no one any good when it’s locked away in a cabinet, or forgotten in the excitement of design.
Daily Tasks and Deliverables
Every UX project is different, and the tasks that one researcher takes on will differ from those appropriate in another setting. Some of the most popular forms of research are interviews, surveys and questionnaires, card sorts, usability tests, tree tests, and A/B tests.
Interviews
One-on-one interviews are a tried and true method of communication between a researcher and a user or stakeholder. There are three main types of interviews, each of which is used in a different context and with different goals.
Directed interviews are the most common sort. These are typical question-and-answer interviews, where a researcher asks specific questions. This can be useful when conducting interviews with a large number of users, or when looking to compare and contrast answers from various users.
Non-directed interviews are the best way to learn about touchier subjects, where users or stakeholders may be put off by direct questions. With a non-directed interview, the interviewer sets up some rough guidelines and opens a conversation with the interviewee. The interviewer will mostly listen during this “conversation,” speaking only to prompt the user or stakeholder to provide additional detail or explain concepts.
Ethnographic interviews involve observing what people do as they go about their days in their “natural habitats.” In this sort of interview, the user shows the interviewee how they accomplish certain tasks, essentially immersing the interviewer in their work or home culture. This can help researchers understand the gaps between what people actually do, and what they say they do. It can also shed light on things that users do when they are feeling most comfortable.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Questionnaires and surveys are an easy way to gather a large amount of information about a group, while spending minimal time. These are a great research choice for projects that have a large and diverse group of users, or a group that is concerned with anonymity. A researcher can create a survey using tools like Wufoo or Google Docs, email it out, and receive hundreds of responses in just minutes.
There are downsides to surveys and questionnaires though. The researcher can’t interact directly with the respondents, and therefore can’t help with interpreting questions or framing them if the wording isn’t quite perfect; and researchers typically have a limited ability for follow up. Surveys see a far higher response rate when they do not require a login or contact information, and this anonymity makes it impossible to ask for clarification or further details.
Card Sorts
Card sorts are sometimes done as part of either an interview or a usability test. In a card sort, a user is provided with a set of terms, and asked to categorize them. In a closed card sort, the user is also given the category names; in an open card sort the user creates whatever categories he or she feels are most appropriate.
The goal of a card sort is to explore relationships between content, and better understand the hierarchies that a user perceives. Many content strategists and information architects rely on card sorts to test out hierarchy theories, or kickstart work on a site map.
Usability Tests
Usability testing involves asking potential or current users of a product or service to complete a set of tasks and then observing their behavior to determine the usability of the product or service. This can be done using a live version of a site or app, a prototype or work-in-progress, or even using clickable wireframes or paper and pencil.
While there are many variations and styles of usability tests, there are three that are commonly used: moderated, unmoderated, and guerrilla.
Moderated usability tests are the most traditional type of test. They can happen in person, or via screenshare and video. Whole usability labs are set up, complete with one-way mirrors for stakeholders to observe, for the purpose of conducting moderated usability tests. In a moderated test an unbiased facilitator talks with the user, reading aloud the tasks and prompting the user to think aloud as he or she accomplishes the tasks. The facilitator’s role is to act as a conduit between stakeholders and the user, phrasing questions to evaluate the effectiveness of a design and testing assumptions while helping the user feel comfortable with the process.
Unmoderated usability tests, sometimes also known as asynchronous research, is conducted online, at the user’s convenience. The tasks and instructions are delivered via video or recorded audio, and the user clicks a button to begin the test and record his or her screen and audio. Just like in the moderated test, users are encouraged to speak their thoughts aloud, though there is no facilitator to ask follow up questions. Unmoderated tests are available through numerous online sites and can be significantly cheaper than moderated tests.
Guerrilla testing is a modern, lightweight take on traditional tests. Instead of renting a lab, guerrilla research is typically done out in the community; users are found at coffee shops or subway stations and asked to complete basic tasks with a website or service, in exchange for a few dollars, a coffee, or just out of the goodness of their hearts. While guerrilla testing is a great option, particularly on a budget, it is best used only for products or services with a large user base. More niche products will struggle to find reliable information from the random selection acquired in guerrilla testing.
Tree Tests
Just as card sorts are a great way to gather information before a website’s architecture has been created, tree tests are helpful in validating that architecture. In a tree test, users are given a task and shown the top level of a site map. Then, much like in a usability test, they are asked to talk through where they would go to accomplish the task. However, unlike in a usability test, the user doesn’t see a screen when they choose a site section. Instead, they will see the next level of the architecture. The goal is to identify whether information is categorized correctly and how appropriately the nomenclature reflects the sections of the site.
A/B Tests
A/B testing is another way of learning what actions users take. An A/B test is typically chosen as the appropriate research form when designers are struggling to choose between two competing elements. Whether the options are two styles of content, a button vs. a link, or two approaches to a home page design, an A/B test requires randomly showing each version to an equal number of users, and then reviewing analytics on which version better accomplished a specific goal. A/B testing is particularly valuable when comparing a revised screen to an older version, or when collecting data to prove an assumption.
People to Follow
Many people have contributed greatly to the field of experience design research. Here are just a few that readers may choose to follow, to learn more. If you are just starting your journey into user experience / UX Design you may be a bit confused by all the terms and methodologies that our out there. https://www.ukmeds.co.uk/ is here to help with their beginner’s guide to UX!
Tools of the trade
User Research has the potential to be a sizable undertaking, sometimes to the point that budgetary and scheduling concerns scare people away. Fortunately, today we often see a more casual, habitual approach. The tools we have available are responsible for much of that shift.
Ethnio
Ethnio was the first moderated remote research software when it launched, and it’s still going strong. Ethnio finds users who are currently using a site or app, and (with their permission) allows interviewers to ask them questions about their experience as they go. It automates many elements of the typical in-person test, including real-time notifications, and paying participants with Amazon gift cards. Ethnio has a fourteen day free trial, and four pricing options, to accommodate businesses of every size.
Optimal Workshop
Optimal Workshop has everything! The full Workshop is a bundle of four research tools, all of which are also available sold separately (and very affordably). Treejack is great for remotely testing information architecture, either to test the nomenclature or the hierarchies themselves. Optimal Sort provides online card sorting, to see how users choose to organize content. Chalkmark offers heat maps of click patterns across a site, and Reframer is a tool for taking notes and identifying themes easily. All come highly recommended.
Learn more about Optimal Workshop
SurveyMonkey
Surveys and questionnaires are great ways to gather information, but they’re most useful when hundreds of responses can be seen at once. Enter SurveyMonkey, an online survey-creation and reporting tool, which allows people to customize and brand their own surveys and then send them out via social media, embed them into websites, or integrate with mass mailings. Utilizing social media marketing for lawyers, SurveyMonkey also allows for easy analysis and reporting when the results come in. It’s available as a free Basic version, or for a monthly fee with additional features.
UsabilityHub
For quick design iterations, gut checks, and clear user feedback, UsabilityHub is an incredible resource for low budget teams. With a super-simple interface (yay!) and fast turn-around times, iterative testing and research is a few clicks away through UsabilityHub.
UserTesting.com
When it’s not possible to schedule a real-time test with users, UserTesting.com is a great way to see how people use a site. Researchers can create a series of tasks, and then receive videos from participants—either pre-chosen, or randomly selected. Researchers are able to see a video of the participant using the site, and speaking aloud to explain what they’re doing. UserTesting.com offers Basic and Pro options, and prices accordingly.
Learn more about UserTesting.com
UserZoom
The good news is, whatever you need, UserZoom has it. Usability testing, both moderated and unmoderated, remote testing for mobile and desktop, benchmarking, card sorting, tree testing, surveys, and rankings: they’ve got it! The bad news, as can be expected with any product this robust, is that it can be overwhelming to learn, and it is expensive. Still, for organizations with the budget to handle it, UserZoom is a solid, effective choice.
Associations and Conferences
In a way, all usability conferences are design research conferences. While the other areas of UX tend to have conferences that cater to their factions, trends, or best practices, researchers are by nature generalists, who seek out ways to learn more about humans and usability. To that end, we recommend a little bit of everything, to keep researchers up to speed.
UI Conference
UIE (User Interface Engineering) puts on an annual conference, bringing together thought leaders and tried-and-true concepts for UX practitioners to learn as much as they can from one another. One great thing about this conference is UIE’s commitment to helping people attend, whether in person or virtually.
More information available at: ui.uie.com/
World Usability Conference
At World Usability Conference, the talks cover all areas of usability, user experience, and customer experience management. People come from around the world, across all industries, to find where we have more similarities than differences.
More information available at: www.worldusabilitycongress.com
Design + Research + Society
Held in Brighton, England, the DRS Conference responds to the questions, “How can design research help frame and address the societal problems that face us?”; “How can design research be a creative and active force for rethinking ideas about Design?”; and “How can design research shape our lives in more responsible, meaningful, and open ways?” By focusing on how design research impacts people in today’s society, they turn a light on the human side of our designs.
More information available at: www.designresearchsociety.org/cpages/conferences
UXPA
The User Experience Professionals Association is open to everyone working in UX. They provide networking and professional development opportunities for UX practitioners around the world, by way of local chapters. If you live in a city, there’s a good chance there’s a UXPA chapter to join! Local chapters often host conferences, sponsor events, and create a network for local UX professionals.
More information available at: uxpa.org
UX Research books
There are many books that focus on interviews, usability testing, A/B testing, and other specific areas of design research. These are just a smattering of books that cover the big picture.



